Refractive Index Enhancement of Polymer Thin Film using Ce, Cu, and Ti Ions
May 2024 - Present, Manuscript in preparation
Under guidance of Professor Nanfang Yu, Columbia University, NY
 Working with Cheng-Chia Tsai, this project investigates metal-ion doping as a solution-based approach to tune the optical response of SU-8 polymer films. Through controlled curing and thermal treatment, it produces uniform, flexible thin films with increased refractive index and subtle color shifts. Ellipsometric analysis and Cauchy/Lorentzian optical modeling are used to extract optical constants, and a preliminary machine-learning framework is being developed to correlate refractive-index trends as additional data become available.
Working with Cheng-Chia Tsai, this project investigates metal-ion doping as a solution-based approach to tune the optical response of SU-8 polymer films. Through controlled curing and thermal treatment, it produces uniform, flexible thin films with increased refractive index and subtle color shifts. Ellipsometric analysis and Cauchy/Lorentzian optical modeling are used to extract optical constants, and a preliminary machine-learning framework is being developed to correlate refractive-index trends as additional data become available.

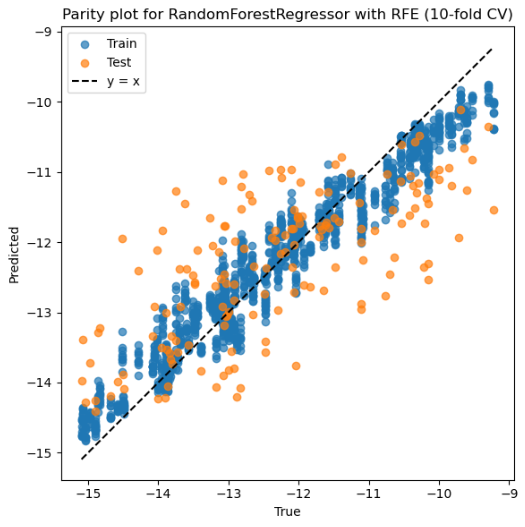 This project, conducted in collaboration with Nicolas Raffaele, draws inspiration from the work of Li-Hui Mou et al. (
This project, conducted in collaboration with Nicolas Raffaele, draws inspiration from the work of Li-Hui Mou et al. ( Working with Cheng-Chia Tsai, this project explores the incorporation of nanocrystalline ceria (CeO₂) particles into polymer matrices to enhance the refractive index for photonic and optical-coating applications. Using ellipsometry and optical modeling, it investigates how nanoparticle loading influences optical constants in flexible, transparent nanocomposite thin films, revealing a nontrivial increase in refractive index while posing challenges for maintaining film uniformity.
Working with Cheng-Chia Tsai, this project explores the incorporation of nanocrystalline ceria (CeO₂) particles into polymer matrices to enhance the refractive index for photonic and optical-coating applications. Using ellipsometry and optical modeling, it investigates how nanoparticle loading influences optical constants in flexible, transparent nanocomposite thin films, revealing a nontrivial increase in refractive index while posing challenges for maintaining film uniformity.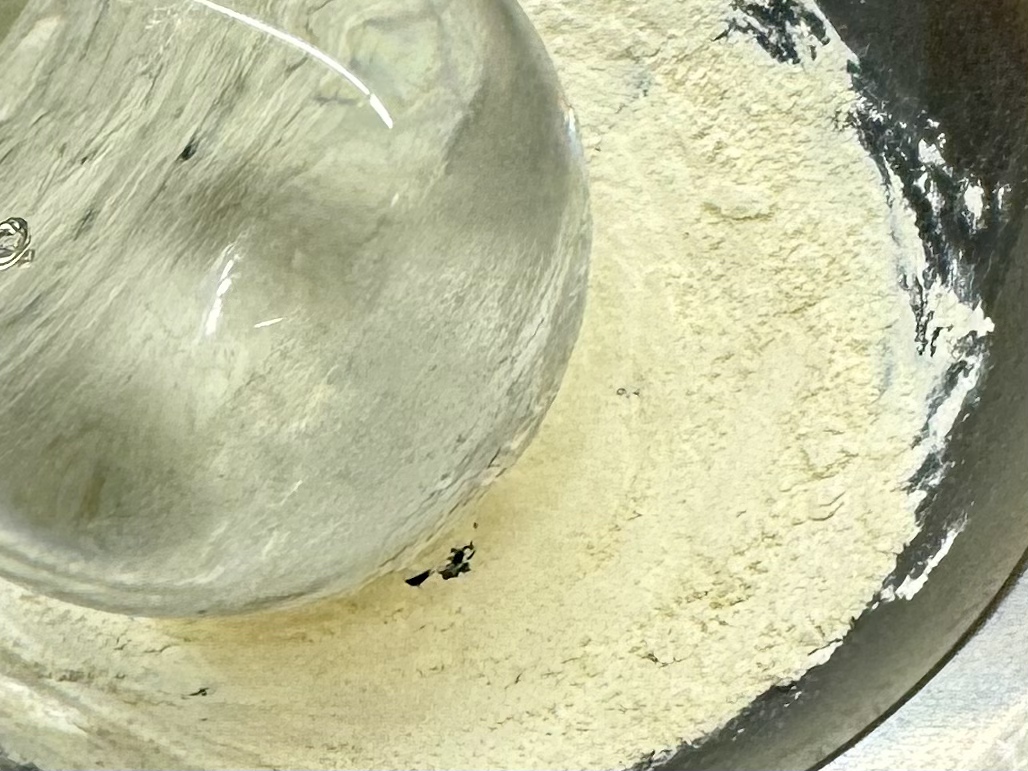 This project, conducted in collaboration with Xinyi Ma, Zhaowen Lin, and Jianing Zhou, investigates small-polaron conduction in copper-doped nanocrystalline ceria (CeO₂). Through impedance spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and structural analysis, it examines how Cu incorporation modifies charge-transport behavior and may interact with local defect chemistry, revealing a measurable enhancement in conductivity compared with undoped ceria, suggesting a possible correlation with oxygen-vacancy dynamics previously reported in high-temperature catalytic studies.
This project, conducted in collaboration with Xinyi Ma, Zhaowen Lin, and Jianing Zhou, investigates small-polaron conduction in copper-doped nanocrystalline ceria (CeO₂). Through impedance spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and structural analysis, it examines how Cu incorporation modifies charge-transport behavior and may interact with local defect chemistry, revealing a measurable enhancement in conductivity compared with undoped ceria, suggesting a possible correlation with oxygen-vacancy dynamics previously reported in high-temperature catalytic studies.